A guide to navigating the future of technology
In today's fast-paced tech world, getting a grip on AI is key. At Fletcher Tech, we're here to make AI easy to understand and use. AI is everywhere—from the apps on your phone to the chatbots you interact with online. It’s a buzzword, a tech revolution, and a driving force behind innovations shaping our world. But what does AI really mean? And how can you get a solid grasp of its fundamental concepts without feeling overwhelmed by the jargon? Whether it's Machine Learning, Generative AI, or the big dreams of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), our guide breaks it all down. Dive in with us to discover what AI is all about, how it works, and what's coming next. Let's explore this exciting field together!
Breaking Down the Basics:
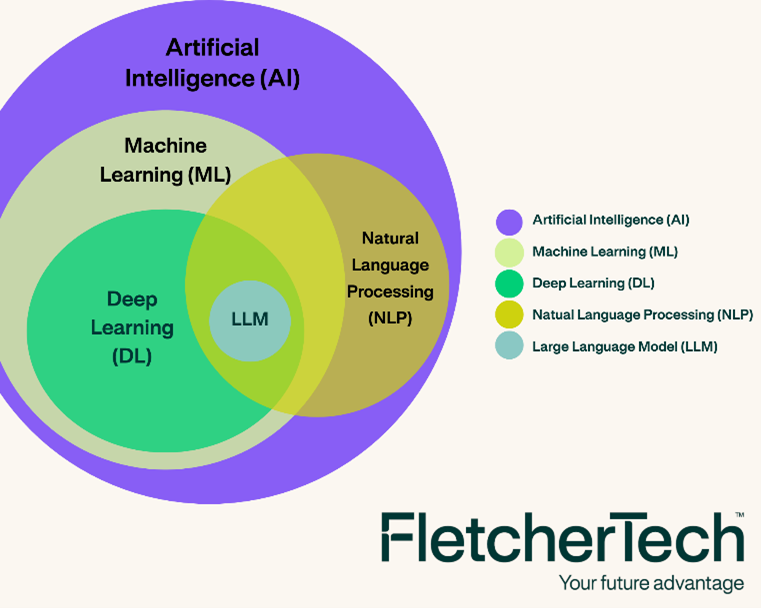
AI, Machine Learning, NLP and Deep Learning
At its core, AI is the science of teaching machines to mimic human intelligence. Within this field, Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP) ,and Deep Learning (DL) are important subfields. Think of ML as a branch of AI that uses algorithms to help computers learn from data and improve over time. DL takes it a step further—it’s a subfield of ML that uses neural networks inspired by the human brain to tackle even more complex problems. DL models can handle vast amounts of data and are particularly good at recognizing patterns, making them powerful tools for tasks like image and speech recognition.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a crucial part of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language. It enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language, making it essential for applications like chatbots and language translation.
Now, enter Generative AI (Gen AI)—one of the most exciting advancements in recent years. It’s a sophisticated application of ML that enables machines to create new content, from text to images to music, based on patterns learned from existing data. To better understand AI, let’s review and explore some key definitions and concepts.
Key Definitions of AI Terms:
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. This includes tasks like decision-making, problem-solving, and natural language understanding. AI allows machines to perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence, whether it’s recommending a movie or driving a car.
Machine Learning (ML)
ML is a subset of AI that focuses on building algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to learn and improve their performance on tasks based on experience. Think of it as training a system to recognize patterns in data so it can make predictions or decisions without explicit programming.
Deep Learning (DL)
DL is a more advanced branch of ML that uses structures called neural networks. These networks mimic the way the human brain processes information, enabling machines to perform highly complex tasks like image recognition, speech translation, or even diagnosing diseases.
Generative AI
Generative AI is an exciting form of AI that focuses on creating new content. Powered by models like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and others, it generates human-like text, art, music, and even code. Generative AI isn’t just mimicking—it’s crafting entirely new outputs based on what it has learned from training data.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a broad field of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. It encompasses various techniques and methods to enable machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
LLMs and Multi-Foundational Models: Understanding the Backbone of Generative AI
When we talk about Generative AI, we often encounter terms like Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multi-Foundational Models. These are the architectures that power Generative AI systems.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are AI models trained on vast amounts of text data to understand, generate, and interact in natural language. Examples include OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard. These models excel in conversational AI, content creation, and information retrieval.
Multi-Foundational Models, like OpenAI’s GPT-4 or Google’s Gemini, go beyond language. They integrate multiple modalities, such as text, images, and audio, allowing them to understand and generate across different types of data. For instance, these models can analyze a picture and describe it in natural language or even generate new visuals based on textual descriptions.
Examples of Generative AI Models by Leading Tech Companies
- Google: Bard, Gemini, Imagen.
- Microsoft: Copilot (integrated into Office 365).
- Meta: LLaMA models for language processing.
- OpenAI: ChatGPT, DALL·E, Codex.
- Innovative Startups: Companies like Stability AI (known for Stable Diffusion) are leading the charge in open-source generative models.
Generative AI has become a transformative technology, not just for big tech companies but also for startups innovating in exciting new ways.
Exploring AGI: The Quest for Human-Level Intelligence
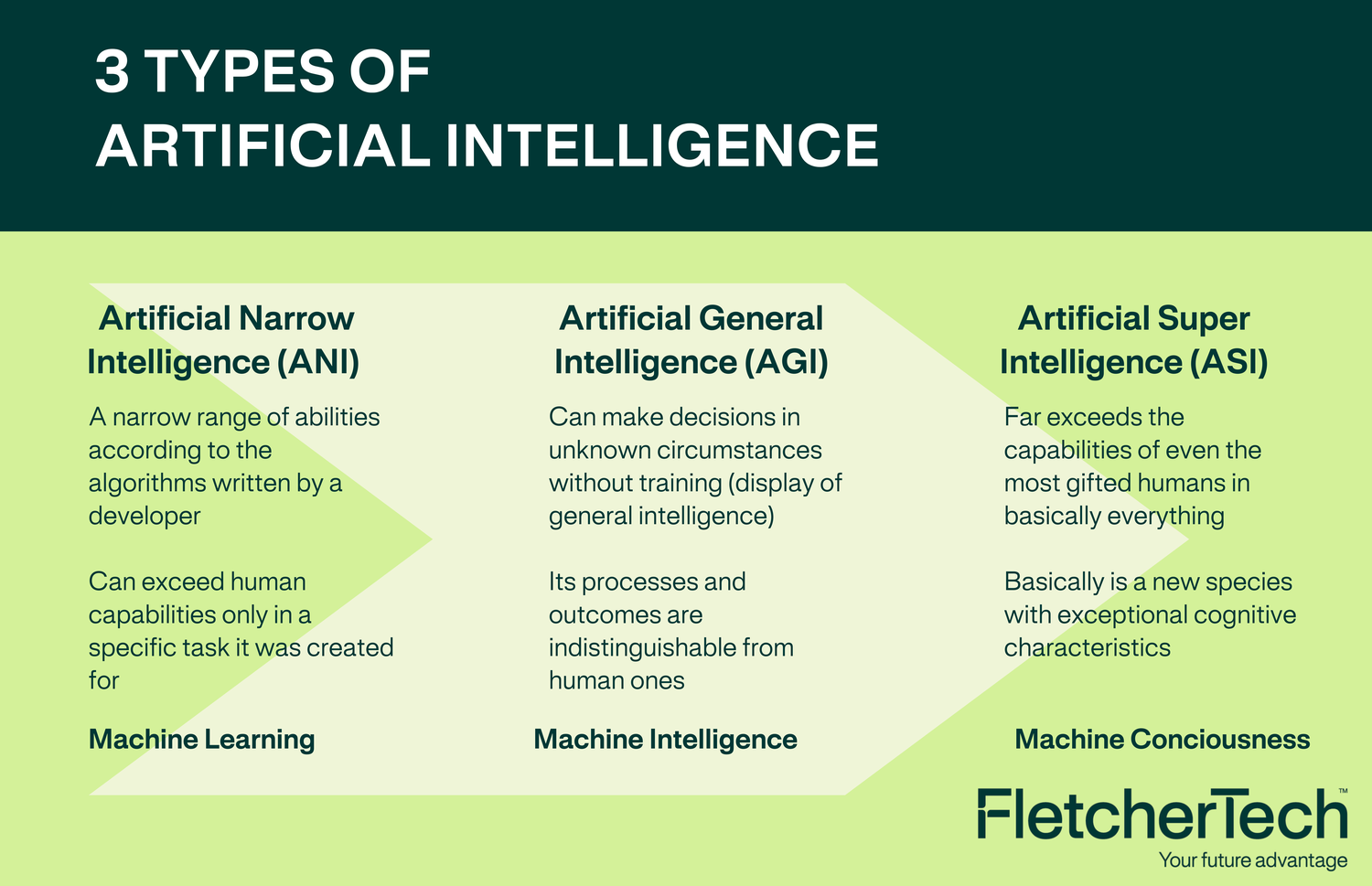
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), or General AI, can be referred to “strong AI,” is the holy grail of AI development. The concept behind AGI is to create machines that can perform any intellectual task that a human can, with the ability to reason, learn, and adapt in a way that mimics human intelligence.
AGI contrasts sharply with Narrow AI, or “weak AI,” which specializes in specific tasks like playing chess or filtering spam emails. While Narrow AI dominates the current AI landscape, AGI represents the dream of creating machines capable of human-like thought processes. Though AGI remains a theoretical concept for now, it fuels much of the ambition and speculation in the AI field. Achieving AGI would be a monumental leap forward—but it also raises profound ethical and societal questions.
Beyond AGI, there's the concept of Superintelligent AI (ASI), which would surpass human intelligence in all fields—this remains purely theoretical.
While Narrow AI dominates the current AI landscape, AGI represents the dream of creating machines capable of human-like thought processes. Though AGI remains a theoretical concept for now, it fuels much of the ambition and speculation in the AI field. Achieving AGI would be a monumental leap forward—but it also raises profound ethical and societal questions.
Responsible AI: What You Need to Know
AI is an incredible tool that’s transforming the way we work, live, and innovate. But with great power comes great responsibility. As exciting as AI is, it’s essential to ensure it’s used wisely and ethically. Here’s what you need to know to navigate the world of Responsible AI in a straightforward, approachable way.
Let’s break down some buzzwords you might hear in discussions about Responsible AI:
• Bias: AI can sometimes deliver skewed results due to biased training data. Imagine teaching a robot to recognize faces but only showing it images from one region—it might struggle to identify faces from other regions.
• Explainability: This is about making AI’s decision-making process clear and understandable. Think of it as peeking into the AI’s brain to see how it’s connecting the dots.
• Black Box: Some AI systems are like mystery machines—you give them input, they give you output, but it’s hard to know what happened in between. That’s what we call a “black box.”
• Overfitting: When an AI model gets too good at memorizing its training data, it might fail to perform well with real-world scenarios. It’s like nailing practice tests but flunking the actual exam.
- Hallucination: This happens when AI generates results that seem convincing but are completely false or made-up. AI does this sometimes, especially when it tries to fill in gaps where it lacks knowledge.
Ethical Principles for Responsible AI
To ensure AI remains a force for good, here are some core ethical principles we should all keep in mind:
- Addressing Bias: Diverse and representative training data is key to minimizing biased outcomes. The more perspectives AI sees, the fairer its decisions will be.
- Privacy: User data should be sacred. Responsible AI development includes protecting data and ensuring it’s used with integrity.
- Accountability: When AI makes decisions—good or bad—it’s critical to know who’s responsible. Developers, organizations, or users must step up and own the outcomes.
- Sustainability: Training large AI models can consume a lot of energy. As we innovate, we need to find greener ways to build and deploy AI.
Why It Matters
By understanding these terms and principles, we can develop and use AI in ways that are ethical, fair, and transparent. Responsible AI isn’t just a checklist—it’s about ensuring AI aligns with human values and serves as a positive force in society.
The goal is simple: let’s create AI that doesn’t just work for us but also works with us to build a better future.
Embracing the AI Revolution
Artificial Intelligence is no longer the stuff of sci-fi—it’s here, transforming industries and reshaping the way we work and live. From understanding key concepts like ML, DL, and Generative AI to exploring the nuances of ethical AI development, getting to grips with the basics is your first step into this exciting world.
Whether you’re a business professional, a tech enthusiast, or simply curious about AI, learning its foundations can empower you to harness its potential responsibly and effectively. Welcome to the future—it’s intelligent, generative, and just getting started!
Kris Yu 16/12/2024